THEORY
Semantic Analysis
Semantic analysis is the process of drawing meaning from text. It allows computers to understand and interpret sentences, paragraphs, or whole documents, by analyzing their grammatical structure, and identifying relationships between individual words in a particular context.
It uses syntax tree and symbol table to check whether the given program is semantically consistent with language definition. It gathers type information and stores it in either syntax tree or symbol table. This type information is subsequently used by compiler during intermediate-code generation.
Semantic Analyzers generally recognize semantic errors such as Type mismatch, undeclared variables, reserved identifier misuse, etc. Functions of the semantic analyzer include-
Type Expressions
Type Expression is an entity in Compiler Design that denotes the type of a language construct. Type Expressions can be of multiple types such as-
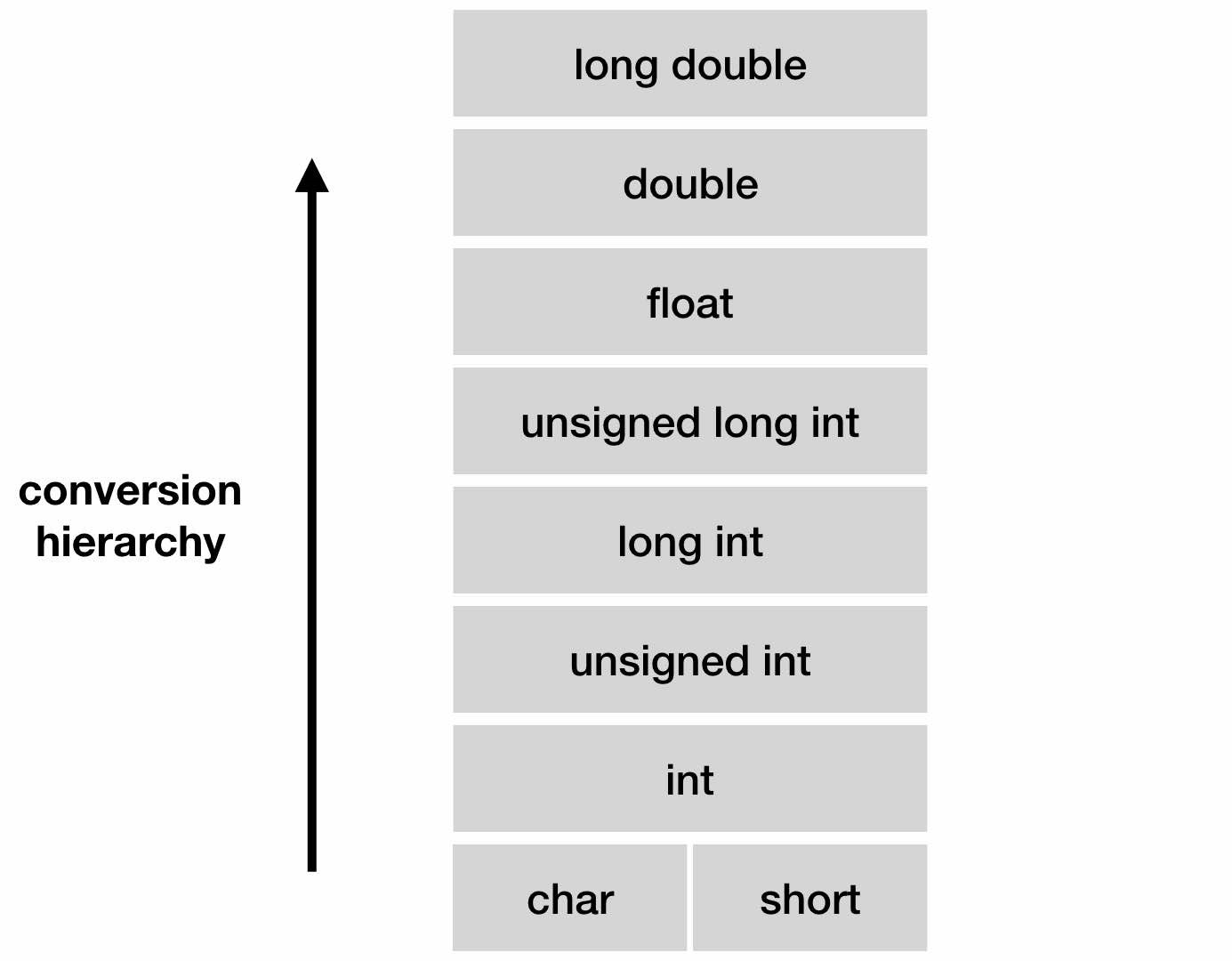
- basic types: int, float, double, char
- formed by applying operators called type constructors to another type expressions
A type constructor applied to a type expression is a type expression.
For example, Array: if T is a type expression then array(I, T) is a type expression denoting the type of an array with elements of type T and index set I.
Type Checking
Type Checking in Compiler Design refers to the process of checking for each operation such that they receive the required number of operands of the proper datatype.
For example, in the expression: A = B * j + d;
* and + are basically int and float data types based operations and if any variable in this expression is of other than int and float then compiler will generate type error.
- for each operation, the number, order and datatype of the arguments are required.
- for each variable, the name and datatype is required.

Type Equivalence
Type Equivalence is the methodology of defining the equivalence of two types. The different types of equivalence that are essential to be considered are:

Type Conversion
The type conversion is an operation that takes a data object of one type and creates the equivalent data objects of multiple types. The signature of a type conversion operation is given as
conversion_op : type1 → type2
If during type checking, a mismatch appears between the actual type of an argument and the expected type for that operation, then type conversion easily converts the data object implicitly and prevents the error. In some languages such as C, type conversion is a built-in function, which implicitly casts an expression to convert it to the correct type. There are two types of type conversions-